Flutter Fare Launch Event
The beginning of a wondrous journey
presented by Jack Frosch

Agenda

- About me and this group
- What you can look forward to
- Your contribution to the group
- A brief introduction to Dart
- A brief introduction to Flutter
About Me










1st Career

About Me
2nd Career

























About Me
My other Meetup

1st Tuesday of the month
About The Group

- Independent Meetup (not Google sponsored)
- Our Meetup is for learning about Flutter and Dart
- Oriented toward Flutter and Dart newbies
- Previous programming knowledge is a prerequisite
- Syntax will be relatable to Java, TypeScript/JavaScript, Kotlin
What you can look forward to

- Flutter and/or Dart Announcements
- Widget-of-the-Week Video(s)
- Dart Language Explorations
- Flutter Explorations and Demos using the Featured Widgets
Some of the topics we'll be covering

Dart
Flutter
- Types and Variables
- Object-oriented Dart
- Async Dart, including Streams
- Interesting Packages
- Much more!
- Widgets galore
- Layouts and Themes
- Navigation
- iOS L&F
- Interacting with servers
- Responsive, adaptive apps
- Much more!
Your contribution

- Presenters wanted
- Backup (co-organizer) needed
- Logistics coordinator needed
A (very) Brief Intro to Dart

- Important language concepts
- A simple program
- Flow control & Exceptions
- Built-in Types
- Lists, Sets, Maps
- Functions & Classes
Dart Language Concepts

- Everything is an object of some class type
- Strongly typed, but supports a dynamic type
- Generics supported (List<String>)
- Functions can be defined at top-level, in a class, or nested
- Variables can be defined at top-level or in a class
- Code organized into libraries we import to use
- Visibility of library items is public or private (indicated with _)
- Variable names start with letter or _, then can have digits
- Expressions have resulting value vs statements which don't
The DartPad

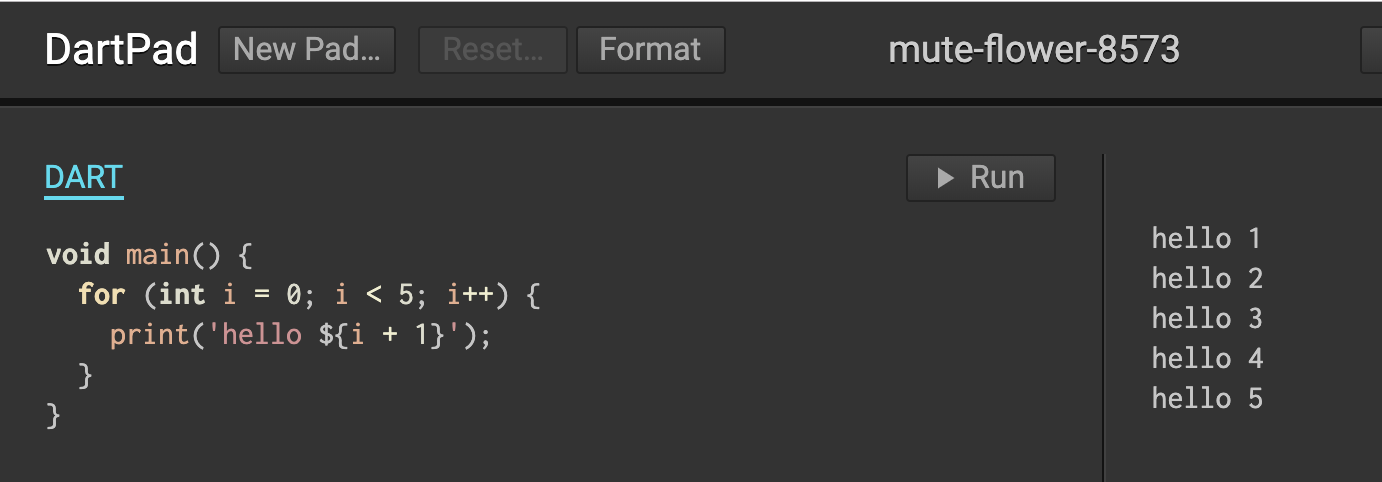

// Top-level function.
int square(int a) { return a * a; }
class SquareUtil {
dynamic squareAnything(dynamic val) {
bool isNumber = val is num // this is how we can do runtime type checking
return isNumber ? val * val : val + val; // ternary operator supported
}
}
// This is the app entry point.
main() {
dynamic result;
var intVal = 9; // Declare and initialize a variable. Type inferred
result = square(intVal); // Call a function
print("Squaring int value ${intVal} yields ${result}");
var sqr = SquareUtil(); // instantiate an object of type SquareUtil
double doubleVal = 2.0;
result = sqr.squareAnything(doubleVal);
print("Squaring double value ${doubleVal} yields ${result}");
String sVal = 'frou';
result = sqr.squareAnything(sVal);
print("Squaring string value '${sVal}' yields ${result}");
}A simple example
Flow Control

- if and else
- for loops
- while and do-while loops
- break and continue
- switch and case
- assert
Dart Types

- numbers
- strings
- booleans
- lists (also known as arrays)
- sets
- maps
- runes (for expressing Unicode characters in a string)
- symbols
Lists, Sets, Maps

- List - unordered, non-unique collection
- Set - unordered, unique collection
- Map - key/value dictionary of entries

void main() {
var list = [ 3, 4, 5 ]; // type inferred as List<int>
var constList = const [ 6, 7, 8]; // const means fixed at compile-time
print("'Classic' C-style for loop");
for (int i = 0; i < list.length; i++) {
print("list[i] = ${list[i]}");
}
print("\nNewer-style for loop");
for (var value in list) {
print("value = ${value}");
}
list.add(6);
print("\nAdd 6 to the list: ${list}");
var newList = [ 2, ...list ];
print("\nNew list using spread operator: ${newList}");
var newListWithConditional = [
if (newList[0] == 2) 1,
...newList
];
print("\nNew list with conditional entry: ${newListWithConditional}");
var cubes = newListWithConditional.map((it) {
return it * it * it;
}).toList();
print("Cubes of newListWithConditional: ${cubes}");
// constList.add(9); // yields error
}Working with Lists

// Working with Sets
void main() {
var items = { 'A', 'B', 'C' }; // type inferred as Set<String>
print("Items in set: ${items}");
print('\nAdd another String:');
items.add('D');
print("Items in set after add: ${items}");
print('\nAdd one or many:');
var newSet = <Object>{}; // element type explicitly Object
newSet.addAll(items);
newSet.add(5);
print("Items in newSet: ${newSet}");
print('\Remove an item:');
newSet.remove(5);
print("Items in newSet after remove: ${newSet}");
print('\nTry to add a duplicate:');
bool wasItAdded = newSet.add('B');
print("Item was added? ${wasItAdded}\nItems in newSet after trying to add duplicate: ${newSet}");
print('\nMake an immutable set:');
var immutableSet = const { 'X', 'Y', 'Z' };
print("Items in immutableSet: ${immutableSet}");
// immutableSet.add('Q');Working with Sets

// Working with Maps
void main() {
var map = { 1: 'Chocolate', 2: 'Vanilla', 3: 'Strawberry' }; // type inferred as Map<int, String>
print("Created map = ${map}");
print('\nAccess individual entry:');
print("Value for key 2: ${map[2]}");
print('\nAccess missing key:');
print("Value for key 99: ${map[99]}");
print('\nAdd a new entry:');
map[4] = 'Moose Tracks';
print("Map after adding entry: ${map}");
print('\nOutput map using keys and values:');
map.forEach((key, value) {
print("key = ${key}, value = ${value}");
});
print('\nOutput map using map entries:');
map.entries.forEach((entry) {
print("key = ${entry.key}, value = ${entry.value}");
});
print('\nMake a new map out of the old:');
var newMap = Map<int, String>();
newMap.addAll(map);
newMap[5] = 'Mint Chocolate';
print("newMap = ${newMap}, length = ${newMap.length}");
var immutableMap = const { 'A123': 46, 'B456': 78, 'C789': 42 }; // type inferred as Map<String, int>
print("immutableMap = ${immutableMap}");
// immutableMap.remove('B456');
// final immutableReference = immutableMap;
// immutableReference = { 'A': 65, 'B': 66 };
}Working with Maps

// Working with classes and functions
import 'package:flutter_web/foundation.dart';
// main() is the entry point and a top level function
void main() {
print('Output Person using custom toString');
var person = Person(firstName: 'Fred', lastName: 'Flintstone');
print("Person person = ${person}");
print('\nOutput Dog:');
var dog = Dog(person, 'Buster');
print("Dog dog = ${dog}");
print("Dog using properties: name = ${dog.name}, breed = ${dog.breed}, owner = ${dog.owner}");
print('\nOutput Dog created with named constructor:');
var dog2 = Dog.poodle(person, 'Fluffy');
print("Dog using properties: name = ${dog2.name}, breed = ${dog2.breed}, owner = ${dog2.owner}");
print("Is dog a poodle? ${dog2.isPoodle()}");
print("Is dog a pitbull? ${dog2.isPitbull()}");
}
class Pet {
String name;
Pet(this.name);
}
//...Functions & Classes

//...
class Dog extends Pet {
Person owner;
String breed;
Dog(Person owner, String name, [String breed]) : super(name) { // breed is optional
this.owner = owner;
this.breed = breed;
}
Dog.poodle(Person owner, String name) : super(name){
this.owner = owner;
this.breed = 'Poodle';
}
bool isPitbull() {
return this.breed == 'Pitbull';
}
bool isPoodle() => this.breed == 'Poodle';
}
class Person {
String firstName;
String middleName;
String lastName;
Person({@required this.firstName, this.middleName, @required this.lastName});
// instance method
String toString() {
return middleName == null ? "${firstName} ${lastName}" : "${firstName} ${middleName} ${lastName}";
}
}Functions & Classes
A (very) Brief Intro to Flutter

- Intro video
- In Flutter, everything is a widget!
- Getting started
- Creating a new app
- A simple Flutter app using DartPad
- A WIP expense app

Intro Video

Widget of the Week
Getting started

- Install Flutter: https://flutter.dev/docs/get-started/install
- Install IDE: https://flutter.dev/docs/get-started/editor
- Android Studio* (preferred)
- VS Code
- Create a new app (CLI or IDE)
A note about targeting iOS

- First - Android Studio works for both iOS and Android!
- When running an iOS simulator, you need iOS bits
- When deploying to App Store, deployment must be signed with a certificate provided by Apple
- You really need access to a Mac
- Alternative: CodeMagic



Simple App Demo

Flutter on DartPad Demo

Expense App Demo
Be warned: it's a WIP

Summary
- Dart is a very approachable language
- Everything in Flutter is a widget
- You'll need access to a Mac to do iOS testing and deployment*
- It's a great time to start learning Flutter!
Resources
-
Dart
-
Flutter
-
CodeMagic: https://codemagic.io
-
Me
-
Email: jackfrosch@flutterfare.com
-
Twitter: @jackfrosch, @flutterfare
-
LinkedIn: jackfrosch
-
Questions?

Flutter Fare Launch Event
By Jack Frosch
Flutter Fare Launch Event
- 2,258



