The Road from Java to Groovy

About Me










1st Career

About Me
2nd Career


















OCI Grails Team
Legend

Cruisin' to easy migration and interop

Caution for potholes & speed bumps

Stopping for rework or collisions
Legend

Anywhere you see a parrot means this inconsistency with Java will be changing when the new "parrot" grammar changes are available in Groovy 3.0 and maybe as options in 2.5.x
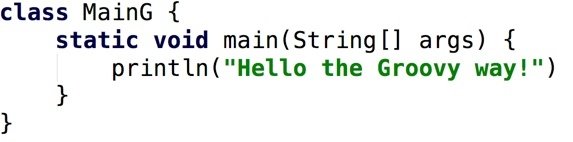
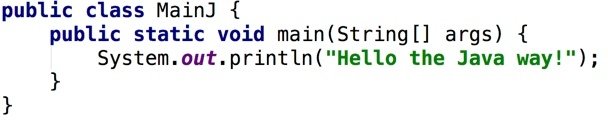


- Generally, migration is very easy
- Often, just renaming the file works
- There are a few roadblocks and detours
Java to Groovy Migration

- Classes
- Interfaces
- Inheritance
- Enums
Groovy OOP like Java

- Kind of like Java 8 interfaces
- Kind of like classes
- Can have state and behavior
Groovy also has traits
trait Singer {
int songLength
void sing() {
println "Oh say can you see..."
}
}
class Teacher implements Singer { }
class Student implements Singer {
void sing() {
println "Twinkle twinkle little star..."
}
}
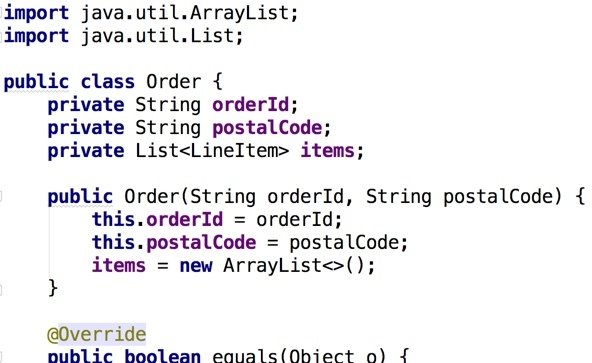
Example: An Order class (Java)


Example: An Order class (Java)


Example: An Order class (Java)

Example: AN Order class (Groovy)
The leftShift method implements << operator overload
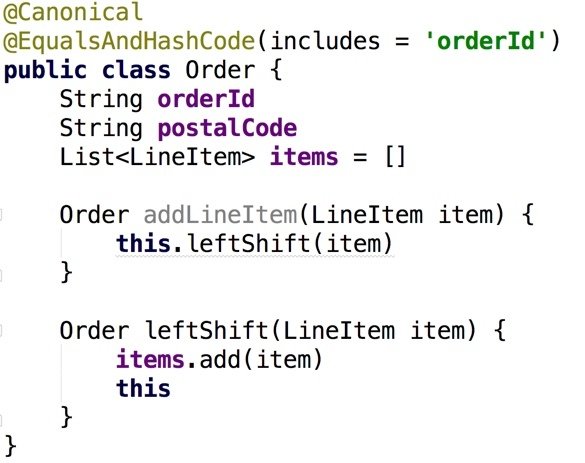
AST transformations are compile time
@Canonical
- Uber AST that wraps three other ASTs
- @TupleConstructor
- @EqualsAndHashCode
- @ToString
- If you also include one of those, it takes precedence


Example: A Line Item class (JAVA)

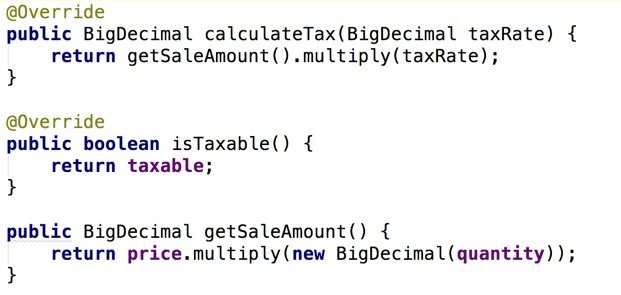
Example: A Line Item class (JAVA)


Example: A Line Item class (JAVA)

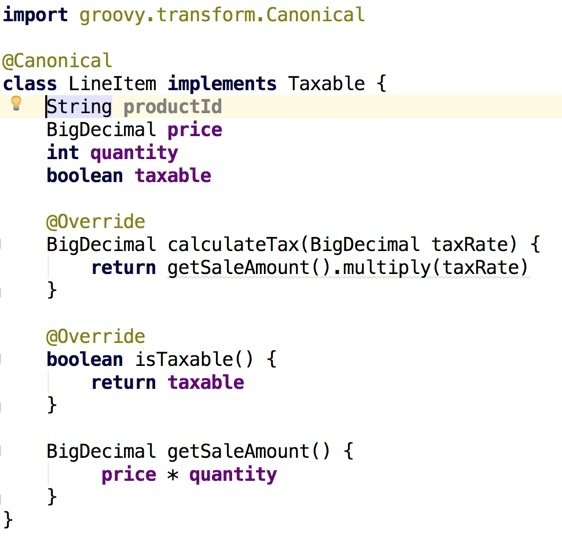
Example: A Line Item class (Groovy)
return is optional
result of last statement is returned

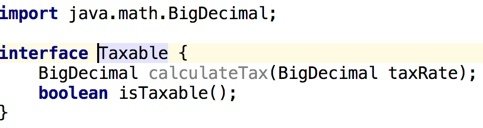
Example: Taxable Interface (Java)
Note: Groovy Taxable interface is nearly identical

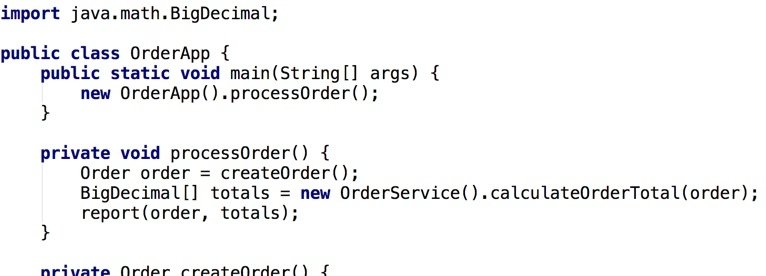
Example: Order App (Java)

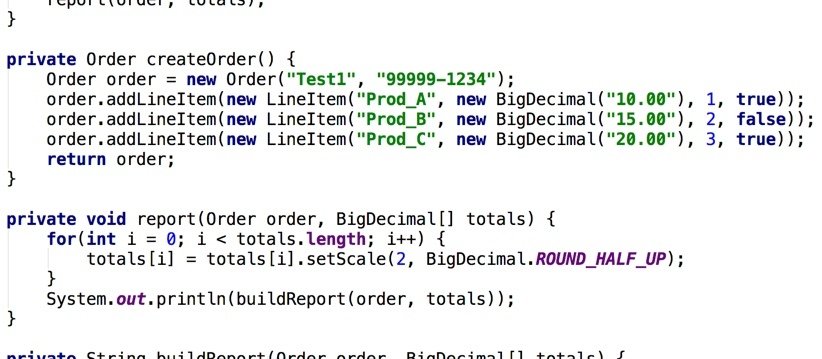
Example: Order App (Java)

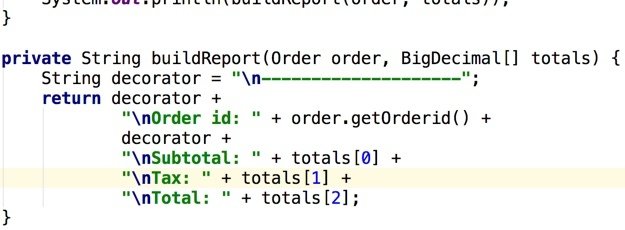
Example: Order App (Java)


Example: Order App (Groovy)

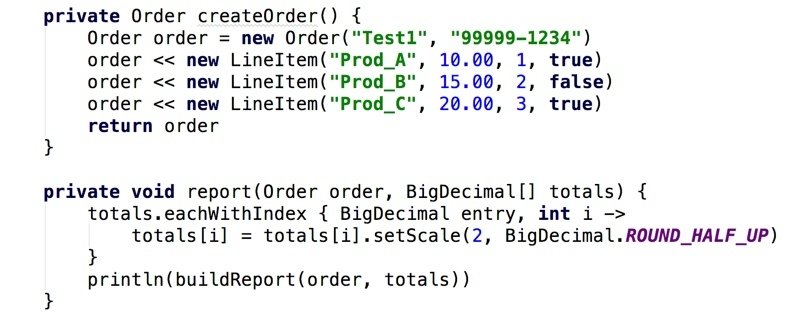
Example: Order App (Groovy)
The Order's leftShift method receives the LineItem

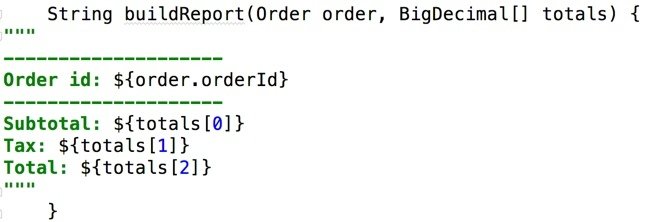
Example: Order App (Groovy)
Triple quotes allow us to easily create formatted, multiline strings
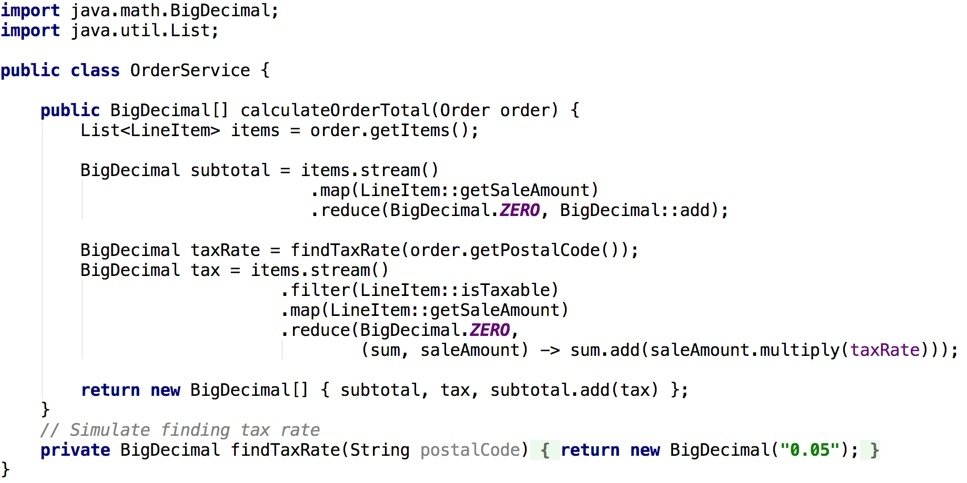
Example: Order Service (Java)
Java 8 introduced streams, method references and lambdas

Groovy doesn't support lambdas and Java method references


Example: Order Service (Java)



Java 8 Gaps in Groovy


- Java 8 introduced major language changes around functional programming
- Functional interfaces with default methods
- Lambda expressions: (a,b) -> a + b
- Method references: BigDecimal::add
- Groovy already had functional idioms
- Does not support lambdas and method references directly

Detouring Around The Java 8 Gaps


- Java 8 method references are a kind of shorthand for lambdas
- Lambdas implement functional interfaces
- Groovy closures can be coerced into meeting contract of the functional interface
- Wherever you find a Java 8 method reference or lambda, you can replace it with a closure
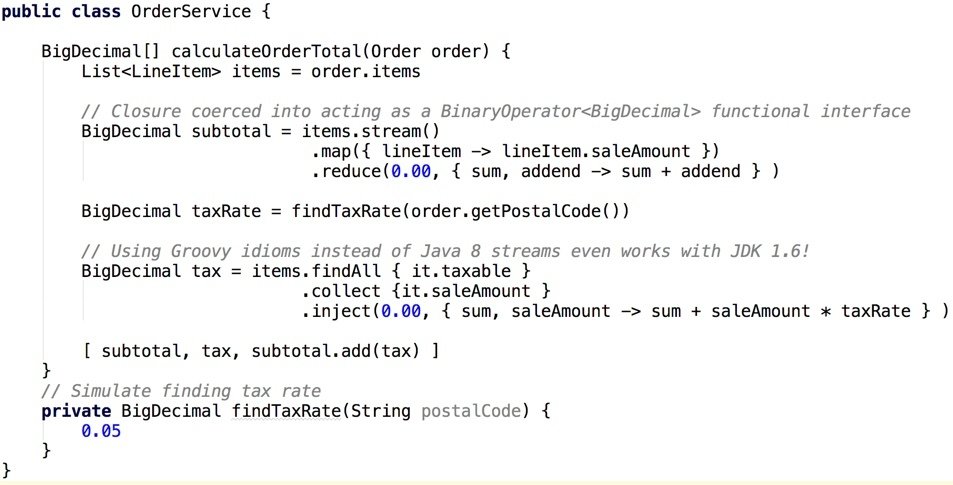
Example: Order Service (Groovy)


Example: Results


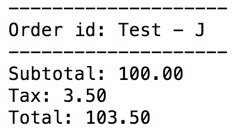
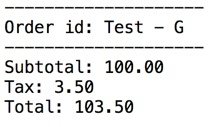
Mostly Smooth running in Regards
to Migration and Interoperability



- Often can simply rename file to .groovy
- Use closures to work around Java 8 gaps
- AST transformations are at compile time, so support interop with Java
Method Dispatching Differences (JAVA)

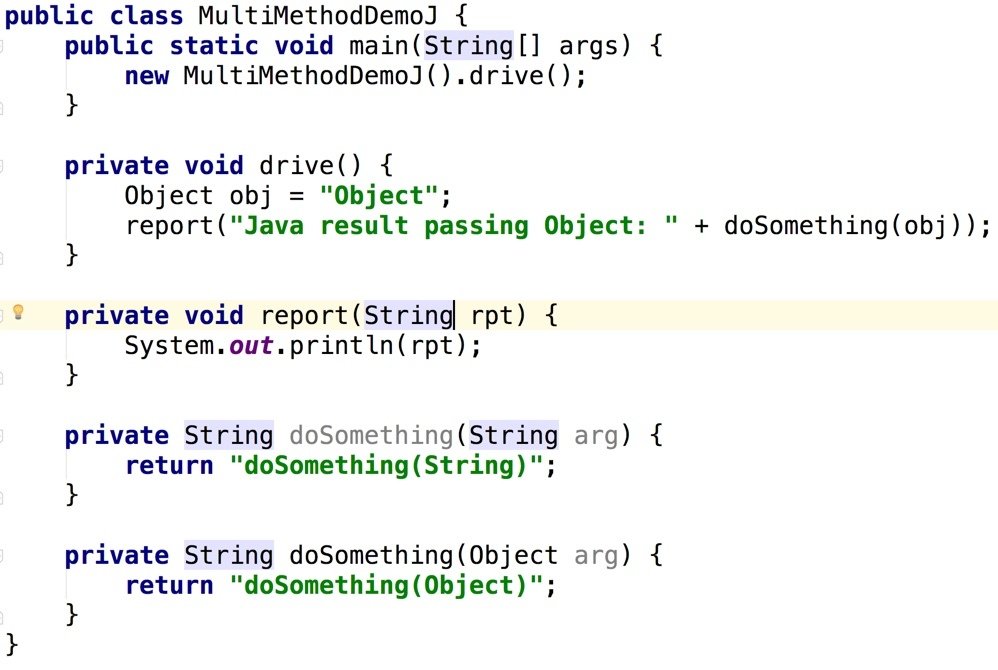

Method Dispatching Differences (Groovy)

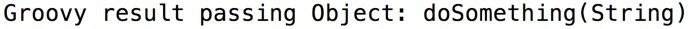

Groovy Equality

== uses compareTo if Comparable, else equals()
<=> 'spaceship' operator
How are two Codes equal?

Groovy Equality


AST transformations happen at compile-time
"spaceship" operator is compareTo
Groovy Equality

Codes equal via compareTo == 0

Groovy Equality


a.is(b)
a === b
Groovy Strings

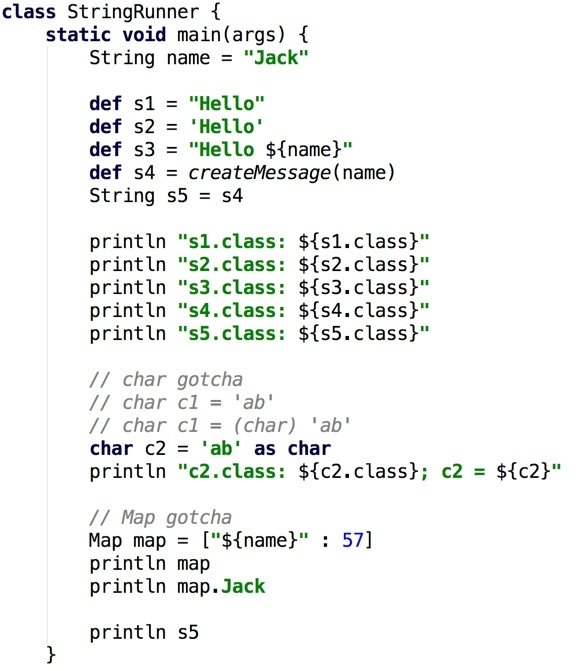
Can be written as map['Jack']
Groovy Strings


Groovy Strings


Map map = ["${name}" : 57]; println map; println map.Jack
Groovy Truth


Groovy Truth

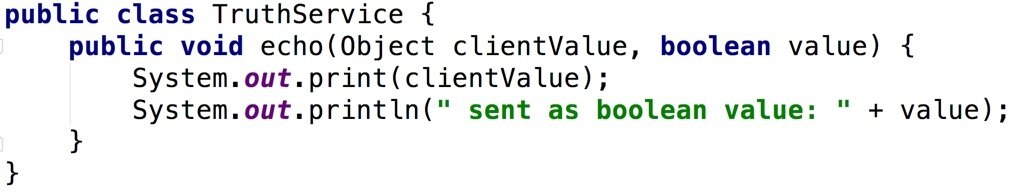
Groovy Truth


asBoolean defines Groovy truth for the object
Groovy Truth

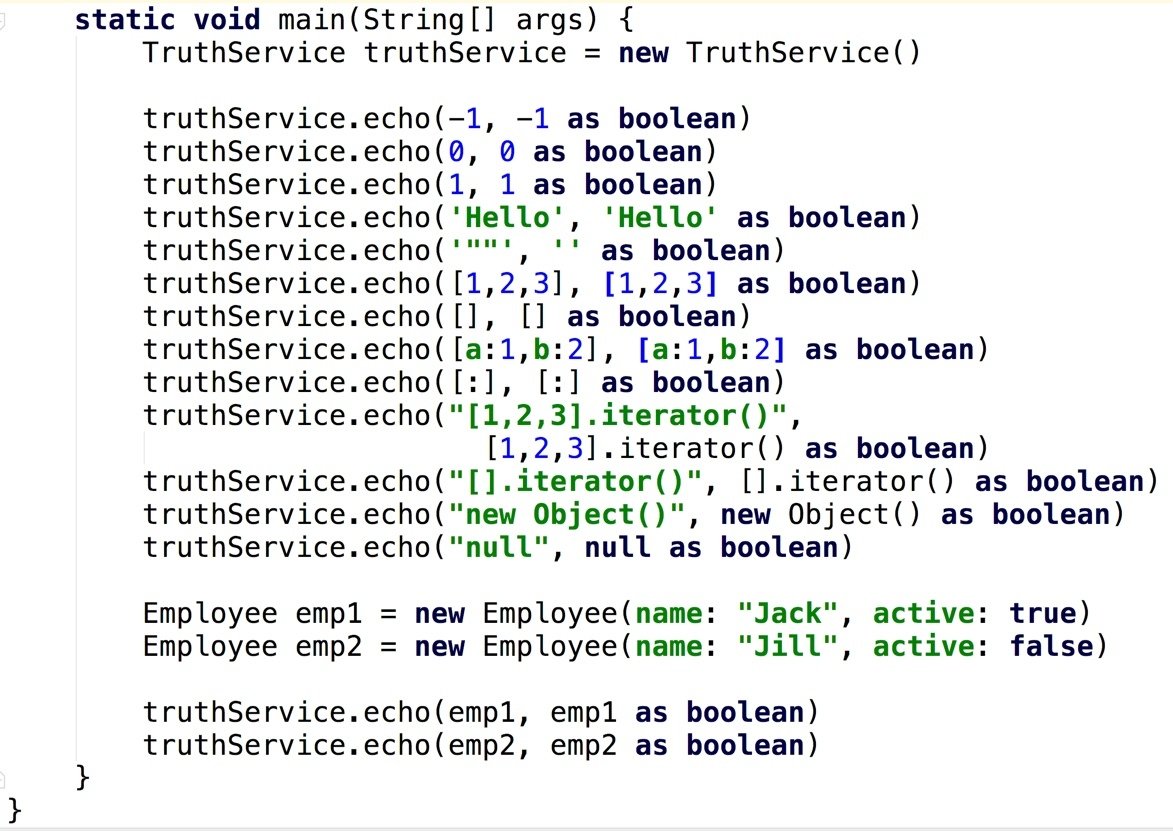
Groovy Truth


Performance (JAVA)
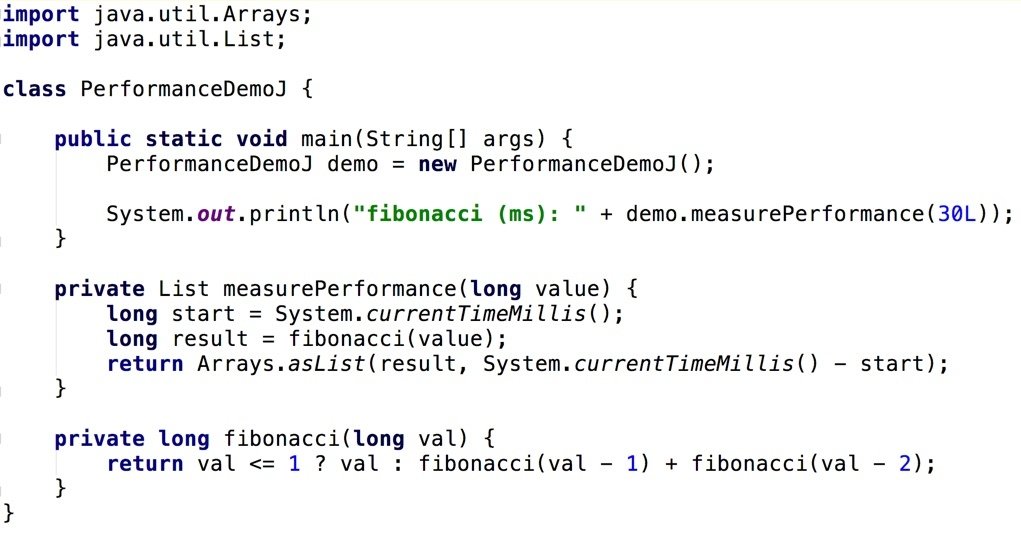
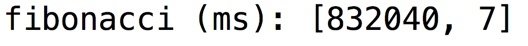

Groovy Dynamic Method Dispatch


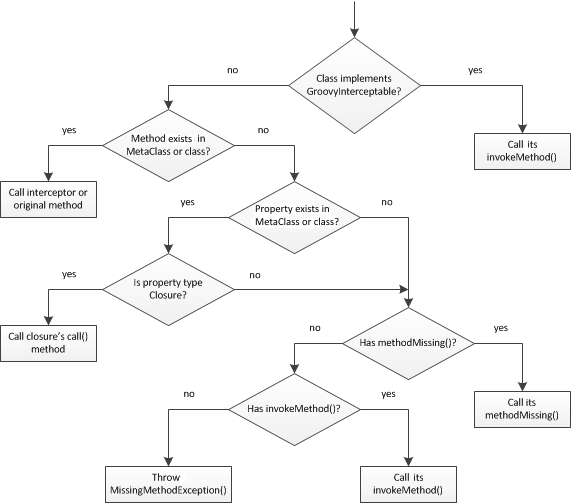

Cruising Performance (Groovy)
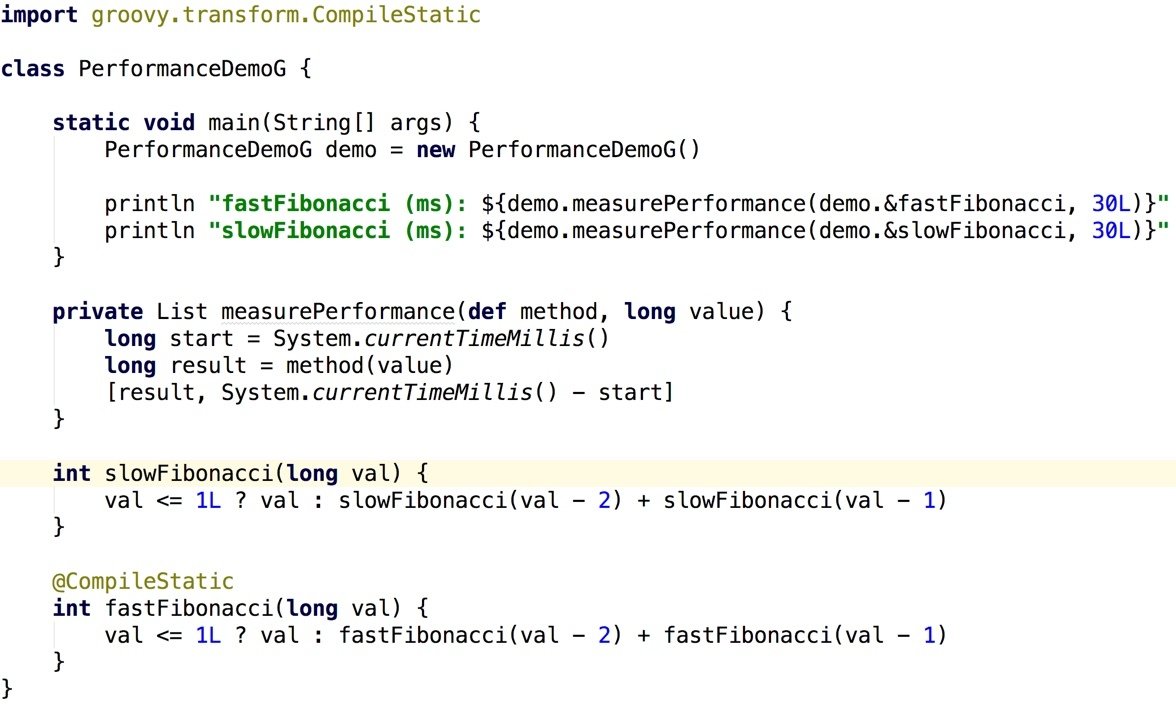
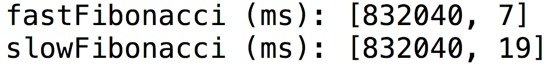
@CompileStatic bypasses Groovy MOP



Note Groovy method pointers
Missing Pavement




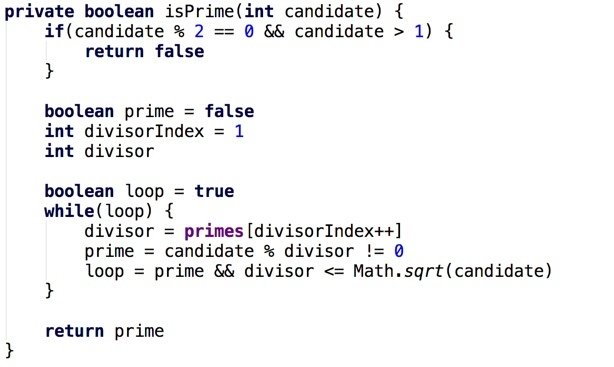
Do / While (Java)




Do While (Java)



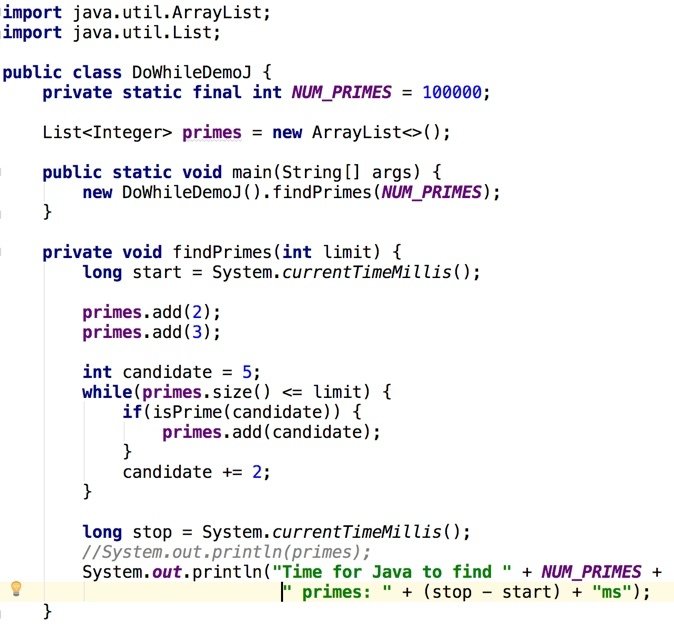
Do / While (Groovy)



Groovy has never supported do/while

To Groovy, do { } looks like do(Closure)
until then...
Do While (Groovy)



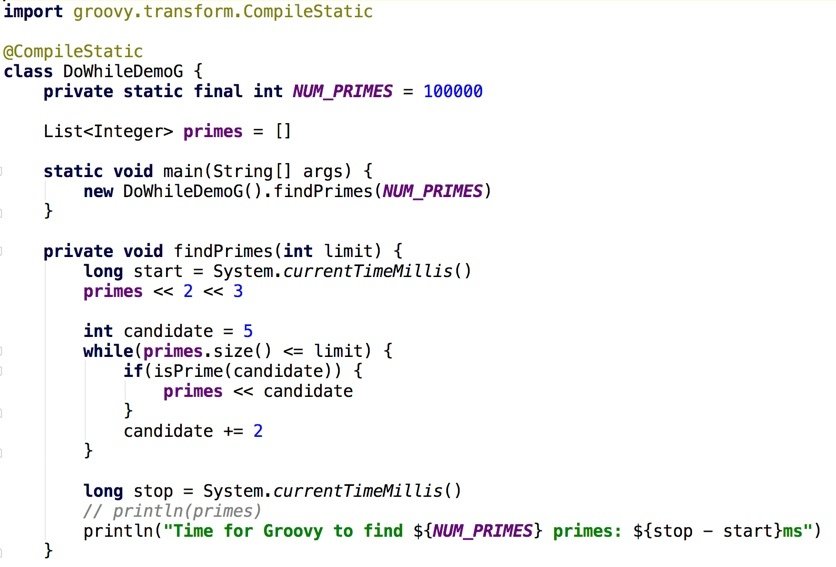
Note @CompileStatic
Do While (Groovy)




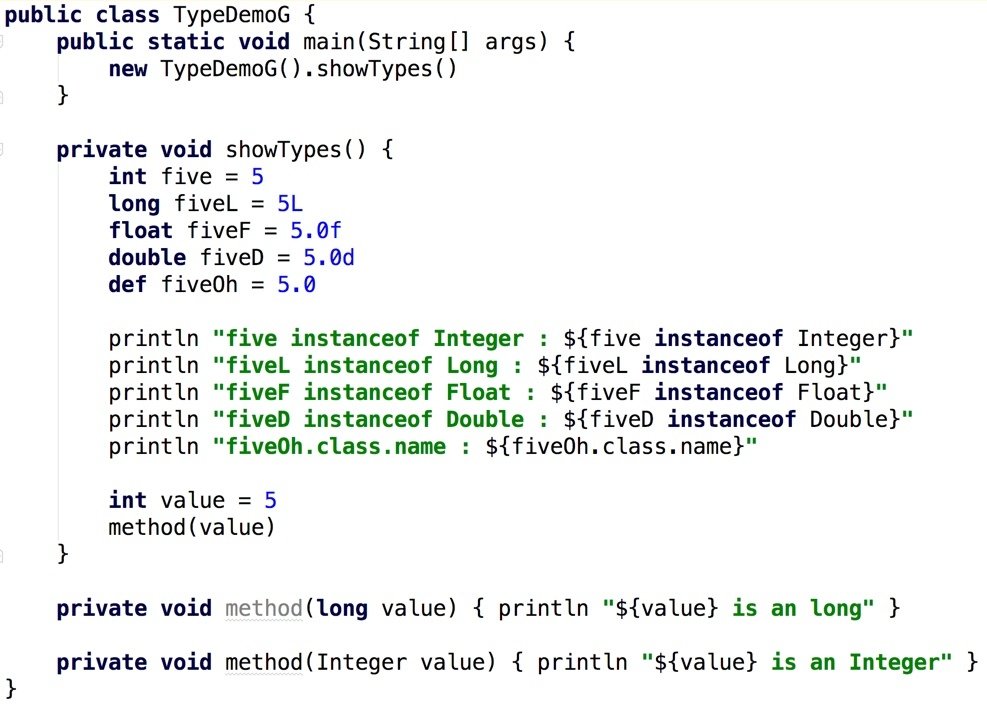
Types (Java)

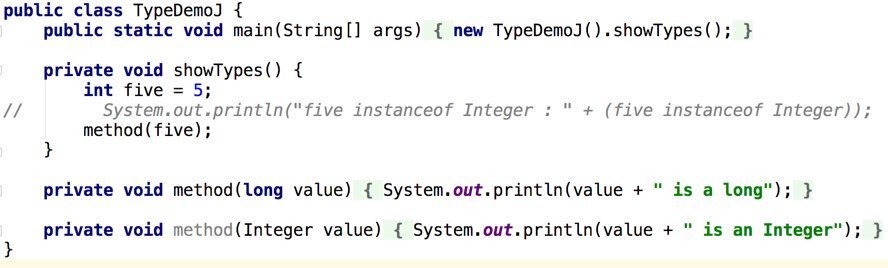
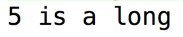
Types (Java)

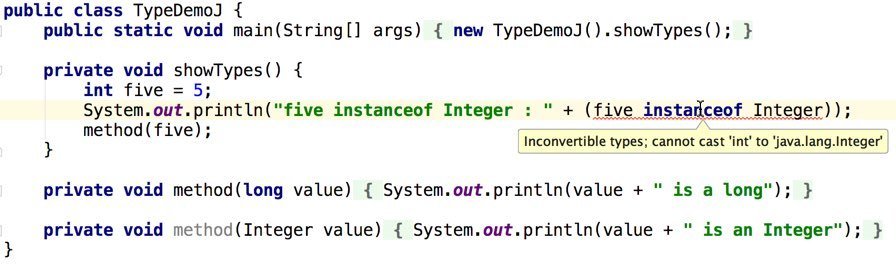
Types (Groovy)


All types in Groovy are Objects
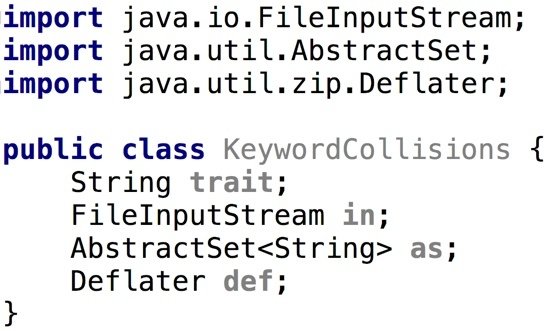
Keyword Collisons


Automatic Resource
Management (ARM) Blocks
Path file = Paths.get("/path/to/file");
Charset charset = Charset.forName("UTF-8");
try (BufferedReader reader = Files.newBufferedReader(file, charset)) {
String line;
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(line);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}- ARM blocks introduced in Java 7
- Goal was to make it easier to ensure resources cleaned up


code from http://groovy-lang.org/differences.html
Groovy Doesn't support Automatic Resource Management (ARM) Blocks
new File('/path/to/file').eachLine('UTF-8') {
println it
}
// or this
new File('/path/to/file').withReader('UTF-8') { reader ->
reader.eachLine {
println it
}
}- Groovy idioms for doing the same thing are even easier
- Meets goal of making it easy to clean up resources


code from http://groovy-lang.org/differences.html

Summary

Migration from Java and interop with Java is almost trivial

There are a few issues arising from the differences between Groovy and Java, but these are easy to remedy

Very few issues are irreconcilable, such as keyword conflicts.
Resources
- What you saw today
- http://groovy-lang.org/differences.html
-
Connect with me
- LinkedIn: jackfrosch
- Twitter: @jackfrosch
- Email: jackfrosch@gmail.com

Thank you!

NFJS - Road from Java to Groovy
By Jack Frosch
NFJS - Road from Java to Groovy
- 5,011



